|
(1) Extended Thermal Shock Immersion Test – IP67
Ref. Exceeds IP67 per standard EN60529
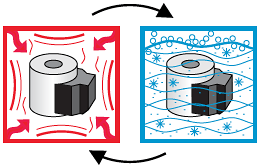
The purpose of this test is to try to induce cracks in the encapsulation of the coil.
The coil is heated for two hours at an ambient temperature of 105°C (±5°C), then immediately immersed in a solution of water, detergent and salt at a temperature of 0° to 5°C for two hours. The coils is then visually inspected for cracks and water penetration. This process is repeated ten times.
(2) Salt Spray Test DIN 50 021 Level 1
Ref: Standard ASTM B117
This accelerated test is designed to simulate the corrosive environment that the coil will encounter during the life of the vehicle.
The coil is subjected to a continuous salt spray as per ASTN B117 for a period of 20 hours. The coil is then rinsed and dried.
(3) Inorganic Dust Test
ANSI/ASAE EP455 Section 5.3
This tests for the effects of dust on the coil.
The coil is placed in a dust chamber containing the equivalent of air cleaner fine dust. Suffi cient air movement is provided to maintain a minimum 0.88g per cubic meter with the coil positioned in its normal mounting position. The test is run for a minimum of 24 hours.
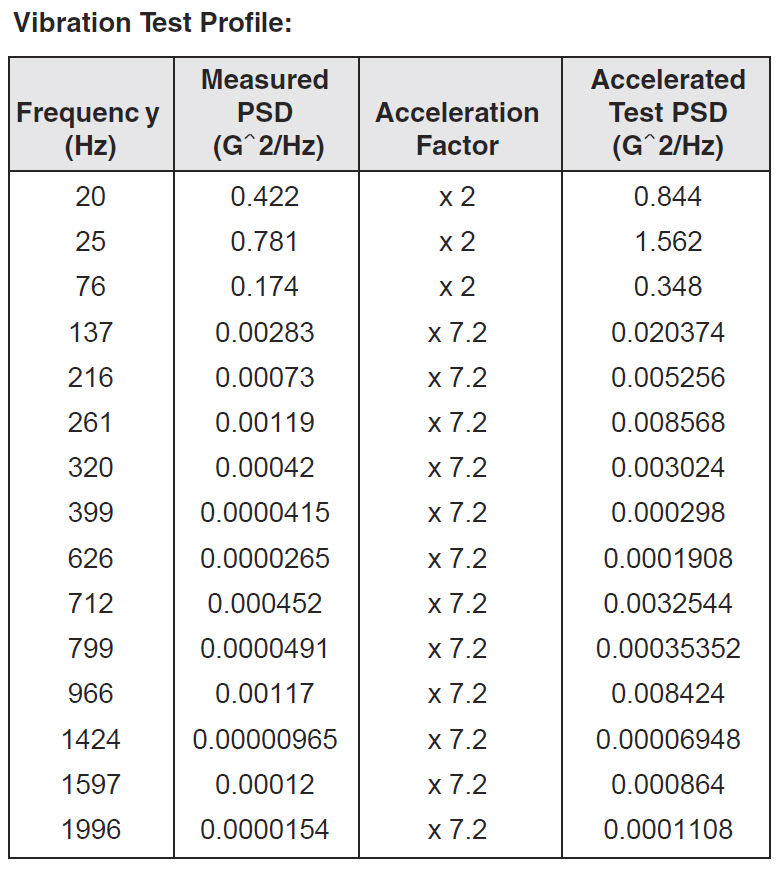
(4) Vibration Test
This accelerated test simulates random vibration that the coil will encounter when used on heavy-duty equipment.
Functional performance is monitored under the following vibration levels shown in the table below for 72 hours in each of the three perpendicular axes. The coil is then checked for impaired function, loose parts and fatigue cracks induced by the test.
(5) Operating Shock Test

This test simulates sudden, severe shock induced when the vehicle is driven over rough terrain.
The coil must withstand a 5ms pulse of 490 m/sec2 (50 g). Impaired function, loose parts, and fatigue cracks caused by this test result in part rejection. The test is repeated a total of five times in each of the three perpendicular axes.
(6) Chemical Resistance Test
• Gasoline
• Engine Oil
• Hydraulic Fluid
• Bearing Grease
• Antifreeze
• Diesel Fuel
• Phosphate Wash
• Degreaser
• Windshield
Washer Fluid
• Battery Acid
• Fertilizer: 28% nitrogen with ammonium nitrate and urea of 5 pH
Coils may be subjected to various chemicals throughout their life. In this test a coil is completely immersed in only one each of the following fluids for a period of 5 minutes. Twelve coils are used at a time. After immersion the coils are heated for four hours at 50°C and the cycle is repeated for a total of ten trials. Impaired function as a result of this test is cause for failure.
(7) Bench Handling Shock Test

This test simulates the effectsmof dropping a coil while it is being handled.
The coil is dropped from a distance of 450mm (±5mm) onto a solid oak bench top at least 44mm thick. The test is repeated by dropping the coil once on all practical edges and faces. Impaired function as a result of this test is cause for rejection.
(8) Storage Temperature Test
This test simulates the effects of storage in extreme temperatures for some time.
While not in operation, the coil is subjected to +105°C and then –55°C for 20 hours each. Impaired function as a result of this test is cause for rejection.
|
|
(9) Humidity Test

This test simulates the effects of relative humidity on the coil.
The coil is soaked at 40°C and 95% relative humidity for 168 hours each while the coil is not in operation. Impaired function as a result of this test is cause for rejection.
(10) Continuous Immersion Test – IP68
Ref. Ref. Standard EN60529
In this test the coil is immersed while powered on.
The coil is immersed in 1 meter of water at an ambient temperature of 25°C (±5°C) for 120 hours while powered according to the chart below. Impaired function as a result of this test is cause for rejection.
(11) Maximum Load Cycling Test
This accelerated test simulates temperature cycling to induce cracks or separation between components of the coil.
Coils are installed in an environmental chamber set to 85°C and 133% of nominal voltage is applied for 1 hour. After 1 hour, the power is immediately switched off and back on within 2 seconds. 133% of nominal voltage is then applied for a period of 5 minutes. After 5 minutes, power is immediately switched off and then back on within 2 seconds. This 5-minute cycle is repeated for a total of 168 hours (power is turned off and on within 2 minutes every 5 minutes). Cracks in the encapsulation, separation in components, or impaired function are cause for rejection.
(12) Jump Start Test
This test simulates the voltage required to jump start heavy equipment.
The coil is thermally soaked in an environmental chamber at 70°C for 2 hours. It is then subjected to 220% of nominal voltage for 5 minutes.
(13) High Pressure Cleaning Test – IP69K
Ref. Standard DIN 40 050, part 9
This test simulates high pressure steam-jet cleaning of a component.
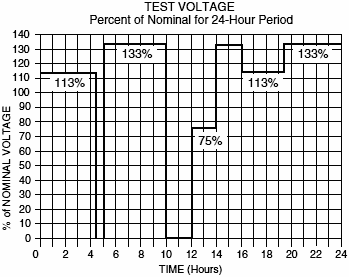
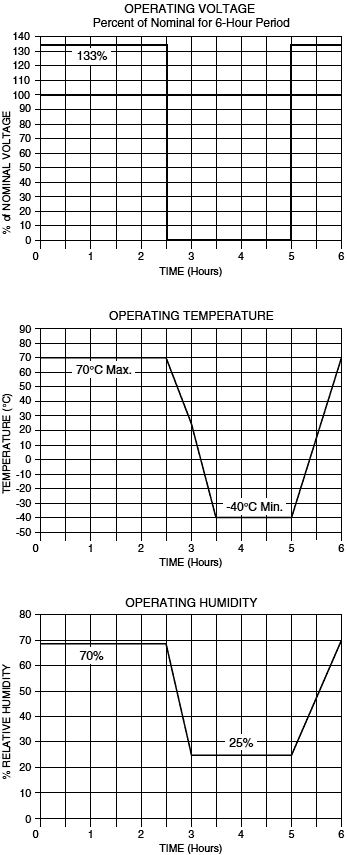
(14) Combined Operating Voltage, Humidity and Temperature Test
This test simulates the combined effects of some of the previous tests.
The coil is simultaneously subjected to the voltage, temperature and humidity profi les shown in the graphs below. The cycle is repeated for a total of 600 hours (25 days). The coils are inspected every 20 cycles for cracks in the encapsulation, separation of components, or impaired function as a result of this test. Any induced flaws will result in rejection.
 |